
Here are six numbers above the median, namely: 34, 42, 54, 56, 61, 65. There are six numbers below the median, namely: 3, 16, 17, 21, 23, 30.

Here are six numbers above the median, namely: 39, 41, 43, 49, 51, 62. There are six numbers below the median, namely: 6, 7, 13, 17, 20, 25. Median = (sixth + seventh observations) ÷ 2 The five-number summary of the data is the median, first quartile, third quartile, First minimum value, and maximum valueĦ, 7, 13, 17, 20, 25, 39, 41, 43, 49, 51, 62.The monthly sales made by David and Bryan are arranged in the table below.Make a box and whisker plots describing the sales made by David and Bryan.

Give a five-number summary of David and Bryan’s sales.Arrange the monthly sales made by David and Bryan in a tabular form.At the end of each month, they record the number of phones sold. Box Plot ExamplesĮxample 1: David and Bryan are both sales attendants at a Phone shop. However, this is most likely not the lowest value in the interquartile range of distribution because there is a high probability that that -100 will be an outlier. Given the dataset -100, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90 for instance, the lowest value is -100. The lowest value, in this case, is not necessarily the lowest value in the dataset.

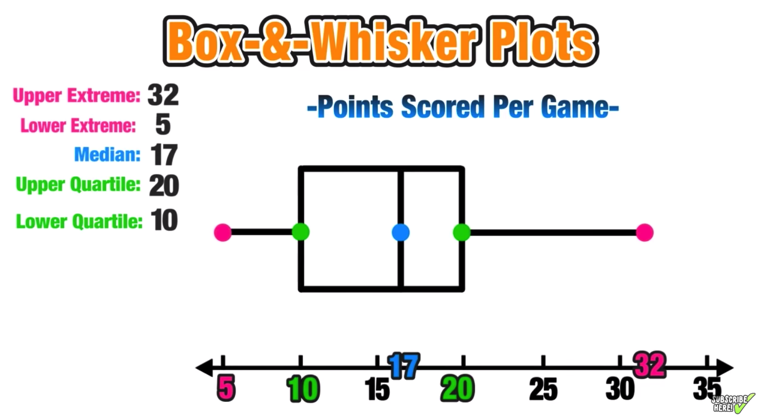
This is simply the lowest non-outlier value in the dataset being visualized by the box plot. However, this is most likely not the highest value in the box plot because there is a high probability that that 1000 will be an outlier. Given the dataset 1,2,3,4,5,1000 for instance, the highest value is 1000. The highest value, in this case, is not necessarily the highest value in the dataset. This is simply the highest non-outlier value in the dataset being visualized by the box plot. It is often said to be a better measure of spread when compared to the range. The interquartile range is the difference between the first quartile and the third quartile. For example, the first quartile of 100 is (¼)*100*3= 75. It is calculated by multiplying the one-fourth of the value by 3. The third quartile is also known as the upper quartile because it is calculated at the 75th percentile. For example, the first quartile of 100 is (¼)*100*1= 25. It is calculated by multiplying the one-fourth of the value by 1. The first quartile is also known as the lower quartile because it is calculated at the 25th percentile. The median is also known as the second quartile. However, when it is even, the median is calculated by finding the average of the two numbers in the middle. The median can be easily formulated when the dataset contains an odd number of values. The median is the quantity that falls in the middle when a set of values are arranged in an ascending or descending order. Although rare, some box plots do not have whiskers. The boxes can either be drawn vertically or horizontally depending on the goal of visualizing the data. That is, the rectangular bars(or boxes), top of the boxes indicating the upper quartile, the bottom of the boxes indicating the lower quartile, the centerline indicating the margin, and the line drawn from each end of the boxes is known as the whisker. The name, box and whisker plot is derived from the nature of the graph. It may also have line extensions extending from the boxes, which usually indicates variability beyond the upper and lower quartiles. Box Plot DefinitionĪ box plot is a statistical data visualization technique that uses rectangular bars to indicate data groups through their quartiles. There are different steps involved in this process, and it will be further explained in the rest of this article. Box & Whisker plots make use of the five-way summary (median, lower quartile, higher quartile, minimum, and maximum) when describing data. Some other methods that require calculation include a histogram, which needs a class interval and a pie chart that requires one to calculate the degree of each slice in the pie.Ĭomputations are no doubt a common occurrence in statistical analysis, but minimal when visualizing data. Box & Whisker plot is one of the few data visualization techniques that perform further computations on the dataset before it can be visualized.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
